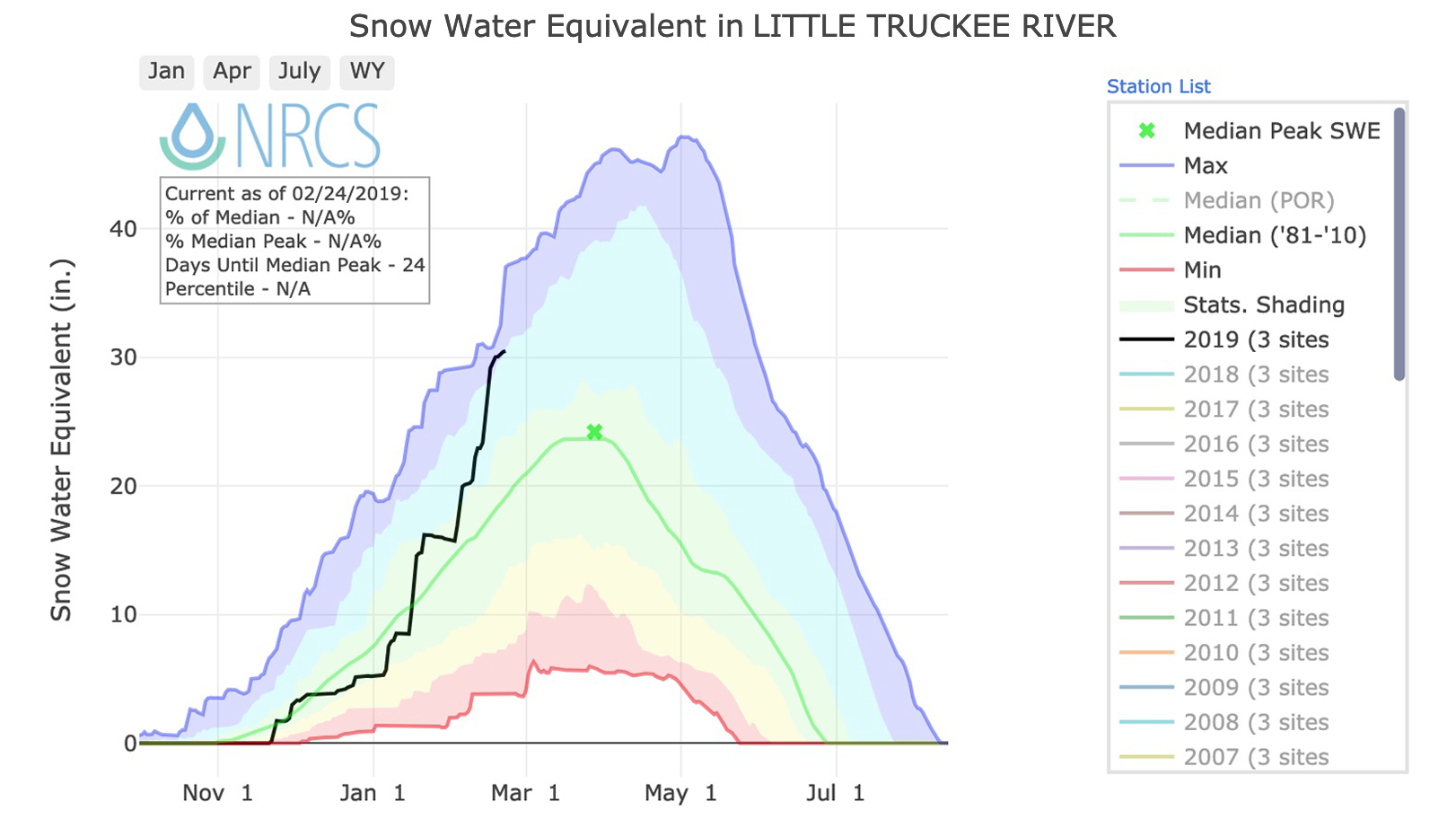
Generate graphs that show cumulative snow water equivalent in river basins in western states of Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming.
Where do these data come from?
A network of Snow Telemetry sites—called SNOTEL—estimates snow water equivalent across basins by weighing the amount of snow that lands on pressure-sensitive snow pillows at stations across the west. Additional measurements come from automated stations and stations where people take manual measurements of snow.
-
How do I use the site?
- Start at the NRCS Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) Interactive Map.
- The map should default to SWE at the basin-level for the most current day, but can be adjusted in the right-hand panel.
- Use your cursor and left-hand navigation tools to locate an area of interest: then click on your desired basin.
- A pop-up will appear. Click the graph to go to an interactive version.
- When the graph shows up, check the legend to make sense of the shading.
- Click various years on the right to compare them with the overall distribution.
- Adjust the time slider at the bottom to examine only a portion of the data available.
-
Data Format(s)PNG
Access Type Link & Description Mapping Pan and zoom to an area of interest, then choose a river basin to see the graph. -
Documentation Type Link & Description General The information comes from snowpack data derived from manually-collected snow courses, automated Snow Telemetry (SNOTEL), and Soil Climate Analysis Network (SCAN) stations. Other data sources include precipitation, streamflow, and reservoir data from the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation (BoR), the Applied Climate Information System (ACIS), the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), and other hydrometeorological monitoring entities. -
Data TypeLand-based station
 Click to see more detail
Click to see more detail